This isn’t just an article but a complete package of the Financial Statements of a company. In addition to the financial statements of a company and books in accounting starting from Journal to Ledger/t account to Trial Balance to Income Statement to Balance Sheet (statement of financial position) to the statement of Cash Flows. This article has also covered the Accounting Cycle as well.
The 𝐀𝐜𝐜𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐂𝐲𝐜𝐥𝐞 – 𝟏𝟎 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩𝐬
The 10 steps of the accounting cycle are as follows;
- The First Step is to Analyze Transactions.
- Second Step is to Prepare Journal Entries.
- Third Step is to Post Journal Entries.
- Fourth is to prepare an Unadjusted Trial Balance.
- Fifth is to Make Adjusting Entries in Journal
- Sixth is to prepare an Adjusted Trial Balance.
- Seventh is to Prepare Financial Statements.
- Eighth is to Prepare Closing Entries.
- Ninth is to Prepare Post Closing Trial Balances.
- Tenth is to Create and Post Reversing Entries.
𝐉𝐎𝐔𝐑𝐍𝐀𝐋
Journal is a physical/digital record that entails financial transactions that we can use for reconciling purposes in the future. It is a book of recording in accounting that we prepare well before the financial statements of a company. We can use this information for other accounting records. i.e. General Ledger. Double Entry Bookkeeping Journal provides the following information;
- Date of Transaction
- Affected Accounts
- Amounts of Transactions
- Detail of Transactions
𝗟𝗘𝗗𝗚𝗘𝗥/𝐓 𝐀𝐂𝐂𝐎𝐔𝐍𝐓
𝗟𝗘𝗗𝗚𝗘𝗥/𝐓 𝐀𝐂𝐂𝐎𝐔𝐍𝐓;
- Is a foundation of a double-entry accounting system, because t account classifies the journal entries and represents the company’s financial data reflecting debit and credit account fields.
- Contains a record of financial transactions and information that is important in preparing financial statements. i.e. income statement, balance sheet, and other reports.
- T account Represents data by type. For instance assets, liabilities, owner’s equity, expenses, and revenues.
- Is also helpful to check errors and to locate the same. As a result, T account helps out to prepare error free financial statements of a company.
𝐓𝐑𝐈𝐀𝐋 𝐁𝐀𝐋𝐀𝐍𝐂𝐄
- Is a worksheet having two columns, Debit and Credit, to ensure the mathematical correctness of ledgers. As a result it helps to detect errors in the double-entry accounting system.
- Shows the ending balance of each ledger account that is the total of all debits and credits.
- is considered to be balanced when the total of debit and credit sides are equal.
- Does not detect the entries that are classified improperly.
- Is prepared periodically usually at the end of the reporting period.
- Trial balance of company plays major role in trasnferring data to financial statements of a company.
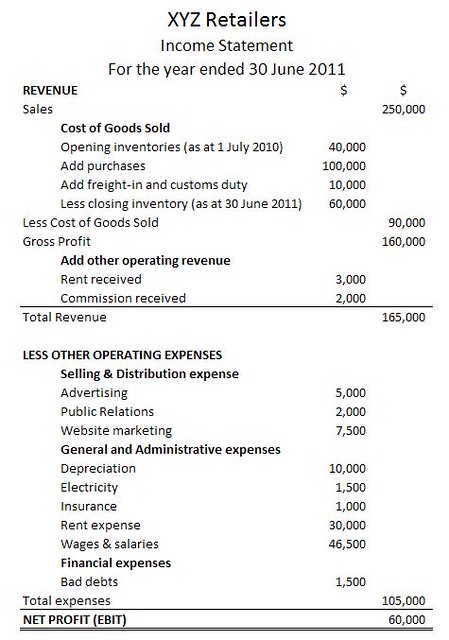
𝗜𝗡𝗖𝗢𝗠𝗘 𝗦𝗧𝗔𝗧𝗘𝗠𝗘𝗡𝗧/𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐏𝐑𝐎𝐅𝐈𝐓 𝐀𝐍𝐃 𝐋𝐎𝐒𝐒
- Is one of the major financial statements.
- Reports the financial performance of a company for a specific period of time.
- Is also called 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝗳𝗶𝘁 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗟𝗼𝘀𝘀 𝗔𝗰𝗰𝗼𝘂𝗻𝘁 / 𝗦𝘁𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗼𝗳 𝗥𝗲𝘃𝗲𝗻𝘂𝗲𝘀 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗲𝘀.
- Focuses on Revenues, losses, Gains, and Expenses.
The formula to compute net income in Income Statement/Statement of Profit and Loss is as follows;
– Net Income = (Total Revenue + Gains) – (Total Expenses + Losses)
– Total revenue = Operating and Non-Operating revenues.
– Total Expenses = Incurred by Primary and Secondary activities.
– Income Statement/Statement of Profit provides critical information to shareholders and management about the following for decision making;
- Firm’s Operations
- Management’s Efficiency
- Sectors requiring attention
- Company’s performance compared to industry peers
– In accrual basis of accounting, it does not differentiate between cash and non-cash receipts/purchases in cash versus purchases on credit.
𝐄𝐗𝐀𝐌𝐏𝐋𝐄 𝐎𝐅 𝗜𝗡𝗖𝗢𝗠𝗘 𝗦𝗧𝗔𝗧𝗘𝗠𝗘𝗡𝗧 / 𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐏𝐑𝐎𝐅𝐈𝐓 𝐀𝐍𝐃 𝐋𝐎𝐒𝐒
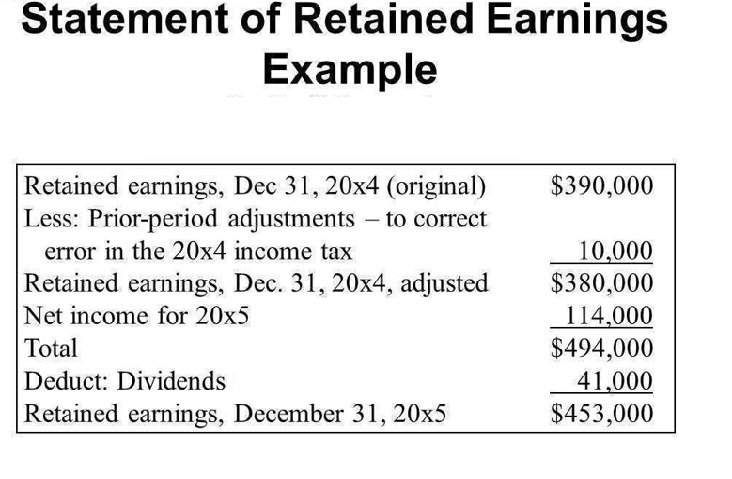
𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐑𝐄𝐓𝐀𝐈𝐍𝐄𝐃 𝐄𝐀𝐑𝐍𝐈𝐍𝐆
– 𝐅𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐮𝐥𝐚 for Statement of Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income/Loss – Cash Dividends – Stock Dividends
Statement of Retained Earnings is a financial statement that;
- Reflects the changes in retained earnings over a specific period.
- Provides information about, how company is treating corporate profits?
- Helps firms to improve investor and market confidence in it.
- Shows reinvestment within the company thru Statement of retained earning.
- Includes information regarding retained earnings, net income, and dividends distributed to shareholders.
The closing balance of statement od retained earnings is the profit that the firm is going to hold because it might;
- Accommodate existing business operations.
- Launch a new product.
- Utilize for possible merger or acquisition and partnership,
- Buy back shares.
- Promote development & growth.
- Repay an outstanding loan. etc.
𝐄𝐗𝐀𝐌𝐏𝐋𝐄 𝐎𝐅 𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐑𝐄𝐓𝐀𝐈𝐍𝐄𝐃 𝐄𝐀𝐑𝐍𝐈𝐍𝐆
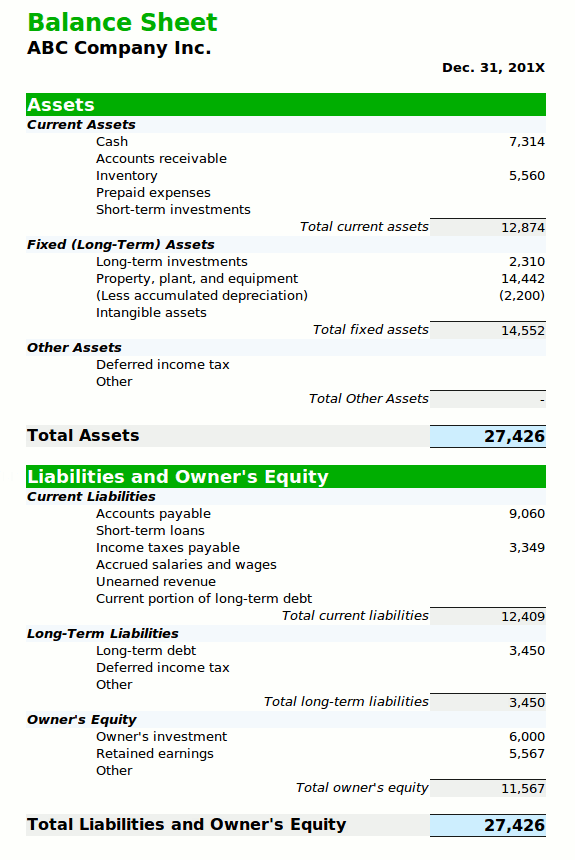
𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐅𝐈𝐍𝐀𝐍𝐂𝐈𝐀𝐋 𝐏𝐎𝐒𝐈𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍 / 𝐁𝐀𝐋𝐀𝐍𝐂𝐄 𝐒𝐇𝐄𝐄𝐓 𝐈𝐍 𝐀𝐂𝐂𝐎𝐔𝐍𝐓𝐈𝐍𝐆
𝐀𝐜𝐜𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐄𝐪𝐮𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholder’s Equity
𝐁𝐚𝐥𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐒𝐡𝐞𝐞𝐭 𝐃𝐞𝐟𝐢𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
Statement of Financial Position/balance sheet in accounting is a Financial Statement because it;
- Shows assets, liabilities and shareholder’s equity on a specific date.
- provides information about what business owns and what it owes on a particular date.
- Discloses total figures of the business concern in terms of total assets, total liabilities and total capital on a particular date.
The statement of financial position/balance Sheet in accounting is a list of Accounts. It has two sides, the right side, and the left side. On one side it shows the accounts having debit balance (assets) while the other side reflects those having credit balances (liabilities & owner’s equity). We can obtain these balances from respective ledger accounts because the closing balances are available there and as a result, the total of two sides will agree.
Firms prepare a statement of financial position/balance sheet to show a business’s true and fair financial position on a particular date. Business people also term it as a Position Statement. The company prepares a statement of financial position/balance sheet in accounting on the last day of an accounting period and reflects the position of only that day because it is ever-changing.
𝐄𝐗𝐀𝐌𝐏𝐋𝐄 𝐎𝐅 𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐅𝐈𝐍𝐀𝐍𝐂𝐈𝐀𝐋 𝐏𝐎𝐒𝐈𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍 / 𝐁𝐀𝐋𝐀𝐍𝐂𝐄 𝐒𝐇𝐄𝐄𝐓 𝐈𝐍 𝐀𝐂𝐂𝐎𝐔𝐍𝐓𝐈𝐍𝐆
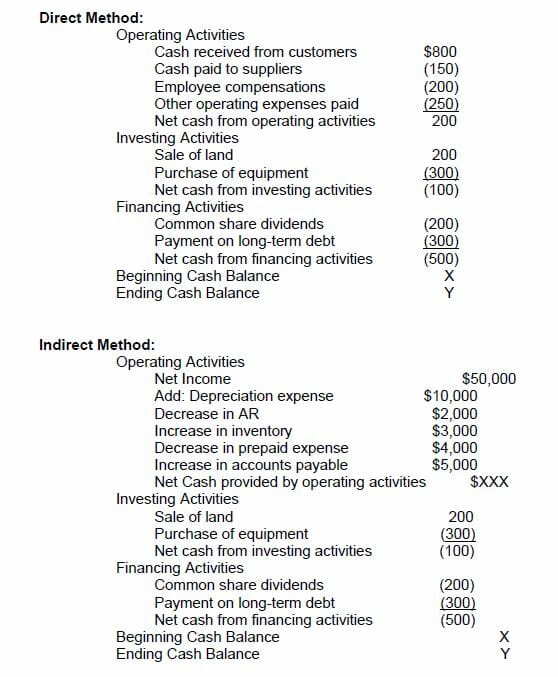
𝐓𝐇𝐄 𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐂𝐀𝐒𝐇 𝐅𝐋𝐎𝐖𝐒
𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐒𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐂𝐚𝐬𝐡 𝐅𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐬 𝐃𝐞𝐟𝐢𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
The statement of cash flows;
- Provides information about all the inflows received by company in shape of cash from its core/ongoing operations or other sources.
- is a important of all financial statements that takes into account the cash outflows that company pays for its business activities and investments.
- Is one of the most essential of all the financial statements because it reflects the cash made by firm via following three activities;
𝐂𝐚𝐬𝐡 𝐅𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐟𝐫𝐨𝐦 𝐎𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬 (𝐂𝐅𝐎)
The first section of the statement of cash flows includes transactions from all operational business activities.
𝐂𝐚𝐬𝐡 𝐅𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐟𝐫𝐨𝐦 𝐈𝐧𝐯𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 (𝐂𝐅𝐈)
The second section of the statement of cash flows is the result of investment gains and losses.
𝐂𝐚𝐬𝐡 𝐅𝐥𝐨𝐰 𝐟𝐫𝐨𝐦 𝐅𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐢𝐧𝐠 (𝐂𝐅𝐅)
The third section of the statement of cash flows provides an overview of cash used from debt and equity.
𝐌𝐄𝐓𝐇𝐎𝐃𝐒 𝐓𝐎 𝐏𝐑𝐄𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐄 𝐓𝐇𝐄 𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐂𝐀𝐒𝐇 𝐅𝐋𝐎𝐖𝐒
𝐓𝐇𝐄 𝐃𝐈𝐑𝐄𝐂𝐓 𝐌𝐄𝐓𝐇𝐎𝐃
Examples of cash receipts and payments include:
- Receipts from customers
- Interest payments
- Payments to suppliers
- Payments to employees
- Tax payments
The advantage of this breakdown is that the stakeholders can have a clear understanding of the business’s ability to manage and generate cash. In addition to the statement of cash flows, they also consider other financial statements while making investment decisions.
𝐓𝐇𝐄 𝐈𝐍𝐃𝐈𝐑𝐄𝐂𝐓 𝐌𝐄𝐓𝐇𝐎𝐃
This method to prepare the statement of cash flows is easier to use, as it banks on data that is already available in the income statement and balance sheet/statement of financial position. Then we adjust net income by converting accrual basis to cash basis by:
- Adding non-cash transactions. i.e depreciation
- Adjusting for changes in balances of current liabilities and current assets (excluding cash) and between the start and end of the period.
The suitable method for you to prepare the statement of cash flows depends on the information you need from the cash flow statement.
𝐄𝐗𝐀𝐌𝐏𝐋𝐄 𝐎𝐅 𝐓𝐇𝐄 𝐒𝐓𝐀𝐓𝐄𝐌𝐄𝐍𝐓 𝐎𝐅 𝐂𝐀𝐒𝐇 𝐅𝐋𝐎𝐖𝐒